Experiment 12 - CAEup: Update of CAE models on actual manufactured shapes
Experiment description
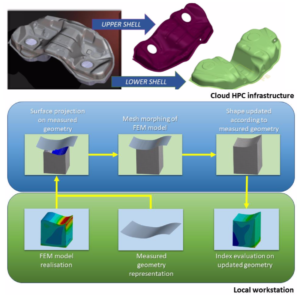
This experiment aims to implement and asses a procedure to offer manufacturing industries a service to enhance the quality control, based on the digital twin concept. The end user provides both the CAE model (digital twin of the nominal design) and the surface representation of the individual measured part. The digital twin is updated on HPC cloud and the performance prediction recomputed adopting a variation of the CAE model shaped as the actual manufactured part.
Description of the envisioned process
The objective is to develop a cloud tool capable to update onto the manufactured shape and the ability to interact with different mesh formats to make the technology solver agnostic.
The performances of the actual component (stiffness strength in this pilot) automatically updated running again the high fidelity CAE and the robustness of the design becomes a quality control which is based on the actual shape of the real component.
Economic impact
The digital twin based process, as a distinctive added value in the competition. CMS aims to offer the new advanced CAE tools/skills as services to their customers that can benefit from digital twin assessed and optimised products. For the tank line, reducing waste rate from 5% to 1% allows to save 484k€/year.
RBF envisions new business opportunities through implementation of both novel and consolidated HPC technologies. The enriched numerical library will be embedded in the full software line.
RINA-C will benefit from the use of the implemented tool by providing CAE services as usual, namely in-site using software and hardware physically present in its premises, and through CloudiFacturing marketplace according to the Software as a Service (SaaS) paradigm.
ANSYS will benefit in consolidating the presence of its tools in an industrial workflow that is supposed to be of interest for a wide range of the engineering market.
In relation to RBF-ANSYS technical collaboration, the improvements of partner RBF tools are a key to offer new functionalities for digital twins.
Technical impact
The representation of a part specific CAE is today possible within the parametric CAD representation of a component. Existing robust design techniques consider variation of nominal design dimensions, for example thickness, a radius, etc. In quality control the assessment (acceptance/rejection) is related to the conformity of controlled dimensions. Advanced surveying systems provide the detailed 3d shape that can be used for:
- a quality assessment related to actual local shape
- update CAE models of the actual shape as quantitative performances evaluators
Experiment Outcome
The CAEUp technology, offered as a cloud service, is a step towards the democratization of advanced simulations. The current implementation, in fact, will facilitate the introduction of advanced CAE according to the Software as a Service (SaaS) model. It will offer a solution for the specific problem tackled, the update of CAE models onto the “as built” shape, but it will open the doors to simulation for actors that at the moment are excluded from such innovation because of the huge investments required in terms of hardware/software and personnel skills. The SaaS model can then turn into a wider adoption of CAE.
Advanced control of shapes offered by CAEUp has the further benefit toward a greener approach: reducing waste allows to save energy and raw materials.










 The project CloudiFacturing receives funding from the European Union’s Horizon2020 research and innovation programme (Grant No. 768892).
The project CloudiFacturing receives funding from the European Union’s Horizon2020 research and innovation programme (Grant No. 768892).
